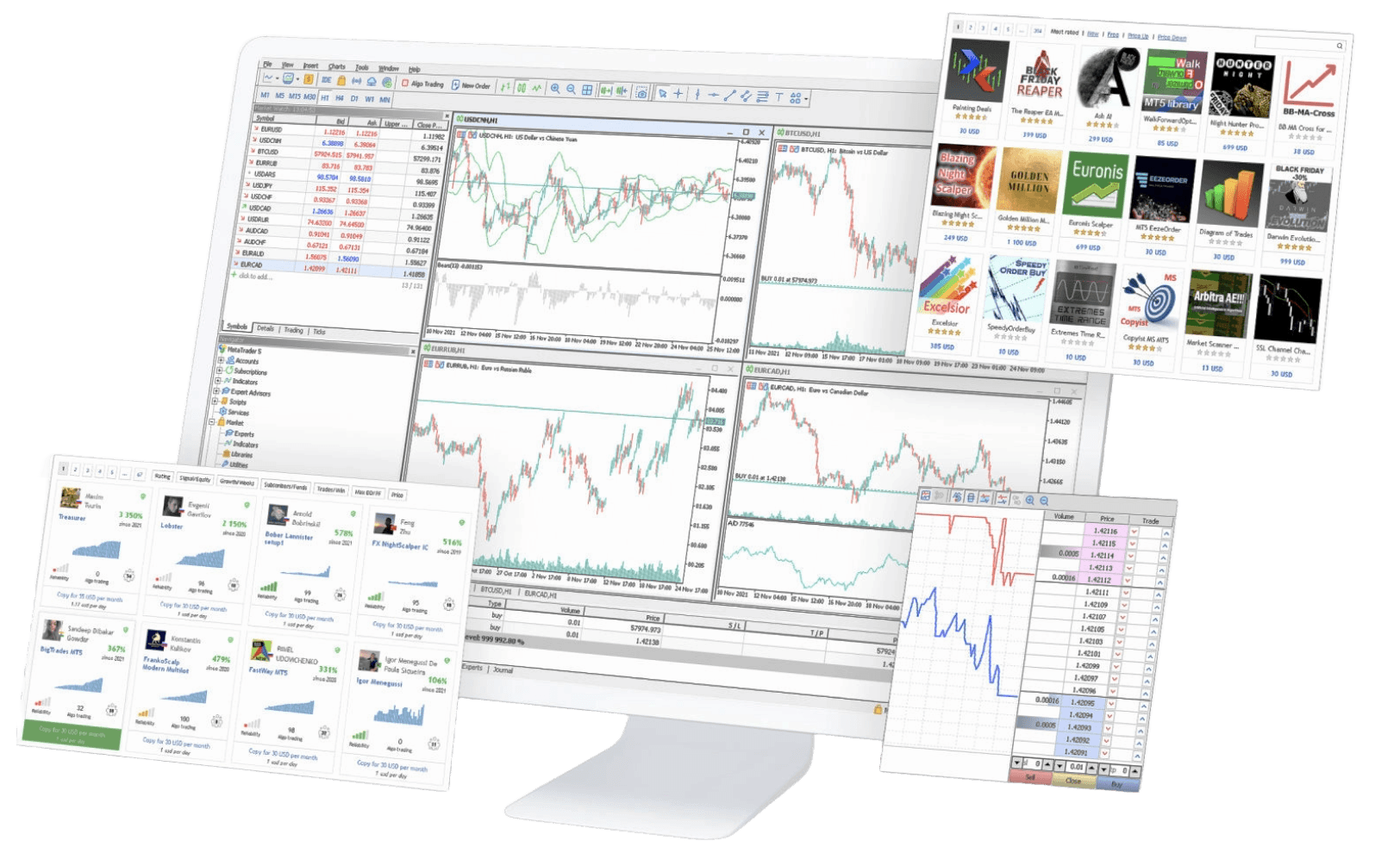
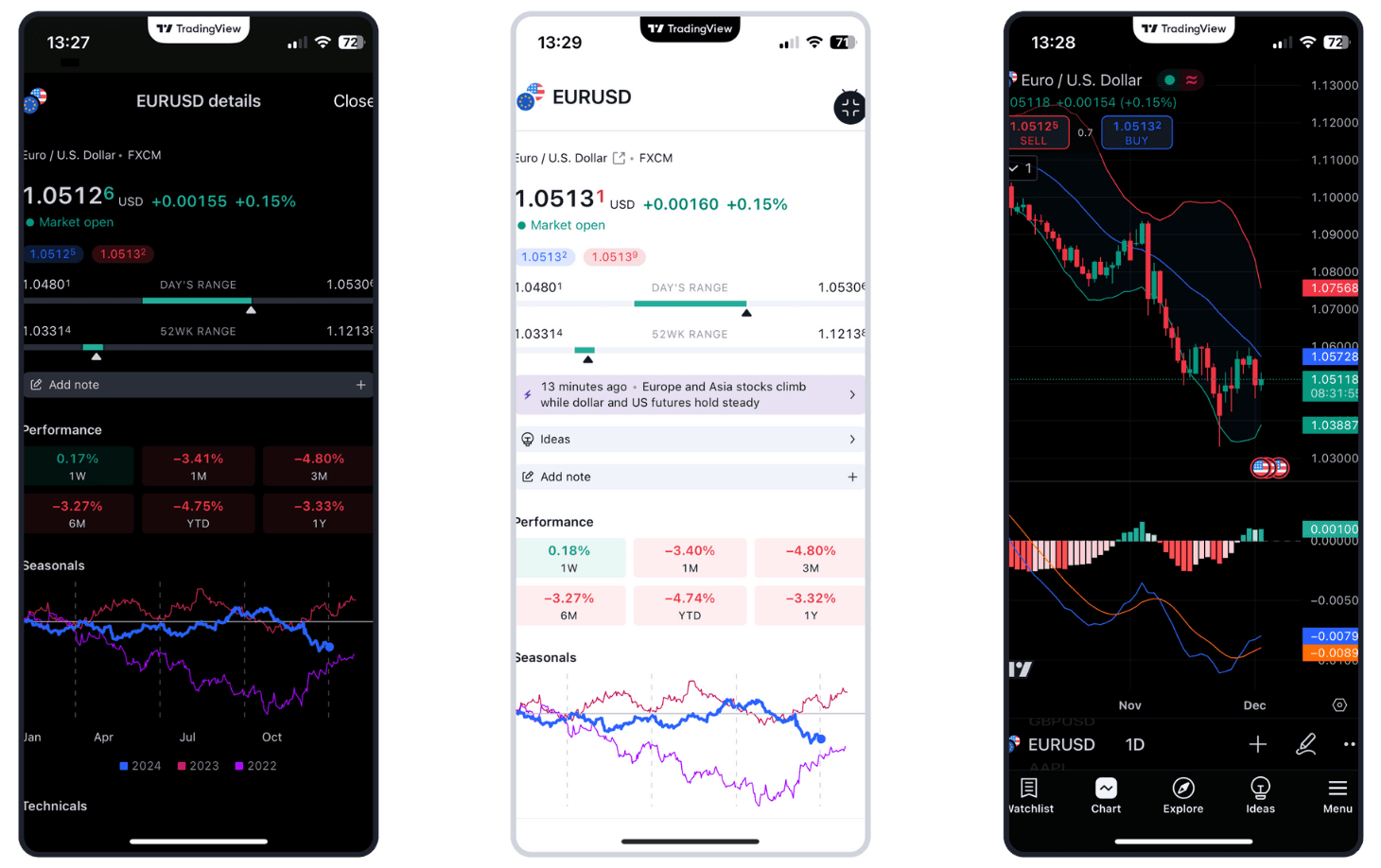
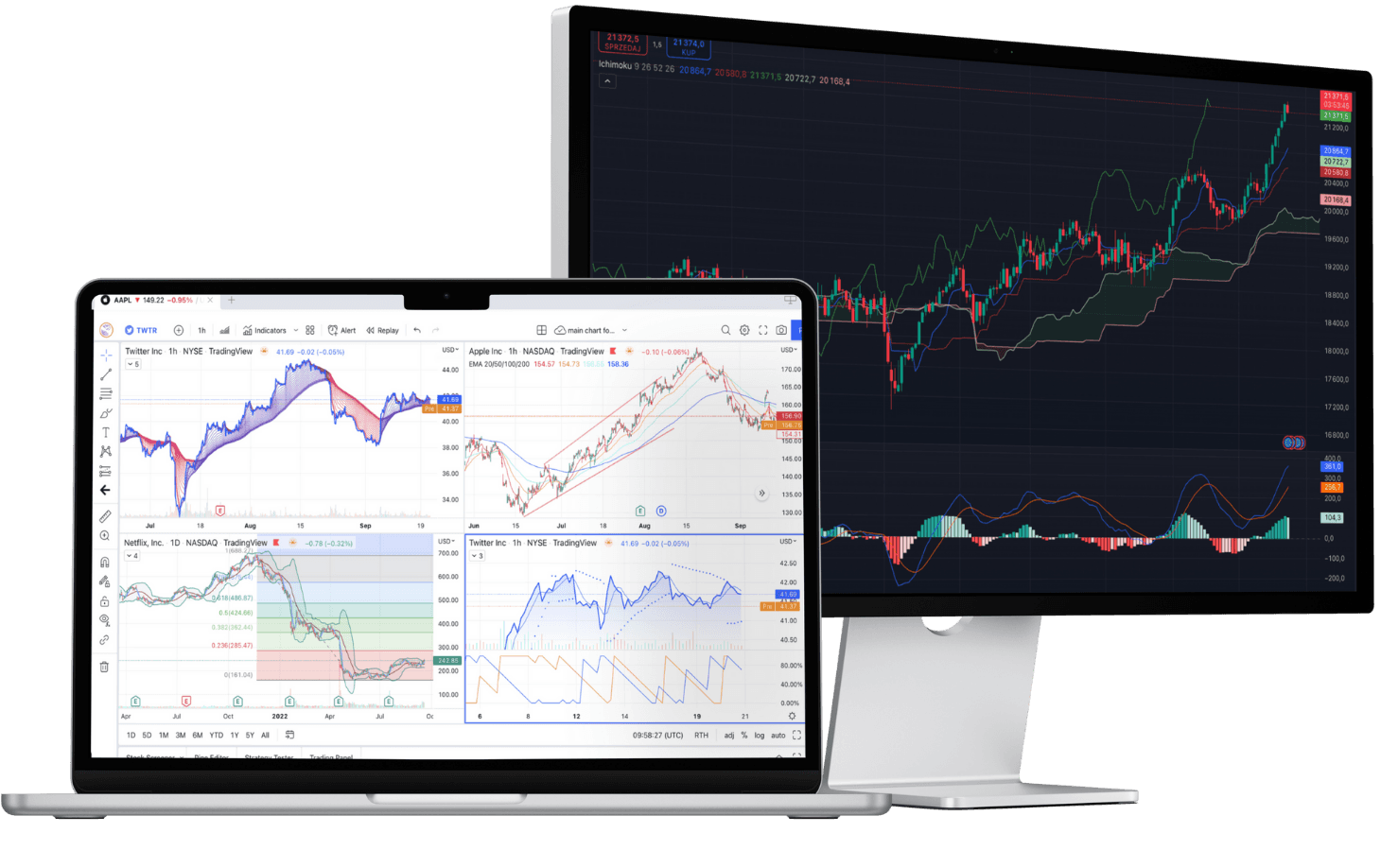
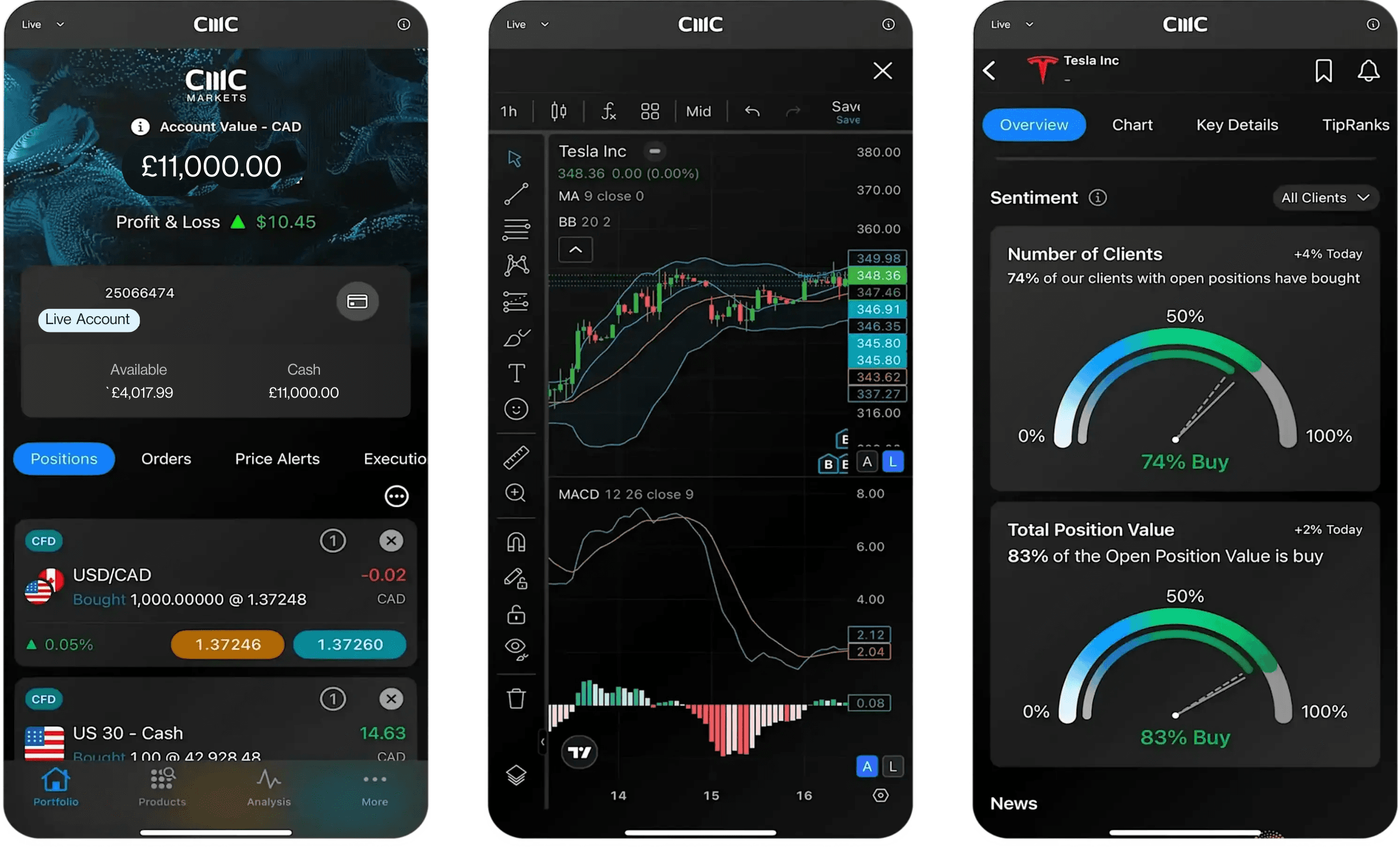
*Trade one-hundredth the size of a standard lot
Instruments
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
Pricing is indicative only. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
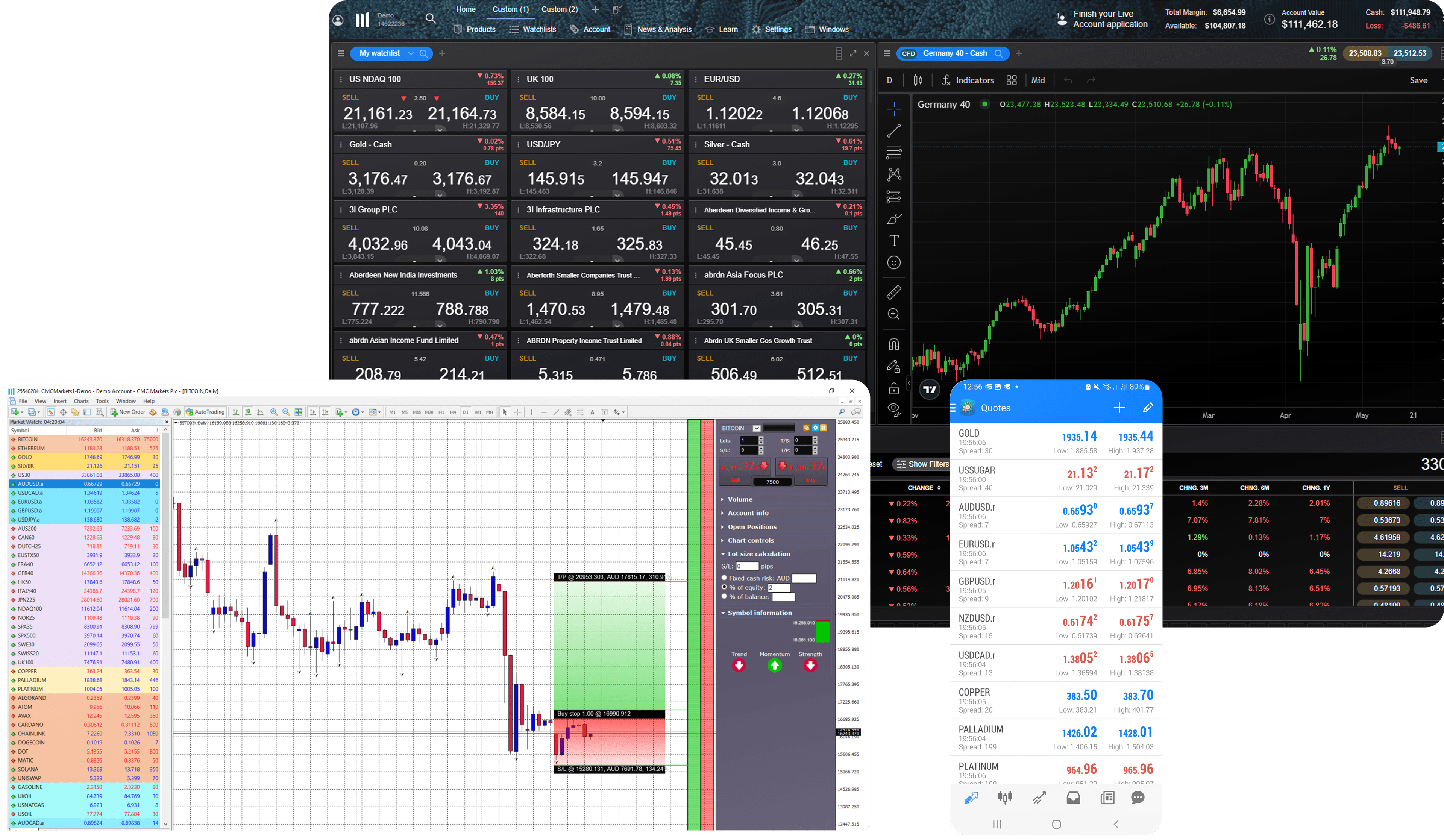
Superior execution and reliability
Our pioneering technology and highly-regarded customer service, alongside a choice of powerful platforms, offers an ideal combination for serious traders.
Join over 2 million global traders and investors
1 Recent awards include: No.1 Most Currency Pairs & Best-in-class for Overall Excellence, MetaTrader, Mobile Trading App, Professional Trading, Research & TradingView, ForexBrokers.com Awards 2026; Best Broker for Active Traders, Professional Trader Awards 2025; Best Mobile Trading Platform and Best Spread Betting & CFD Education Tools, ADVFN International Financial Awards 2025; No.1 for Commissions & Fees, ForexBrokers.com Awards 2025.
2 Based on over 2 million unique user logins across CMC's trading and investing platforms, including partners, as at November 2025.
3 Spreads from 0.0 pips on six major forex pairs, and a 25% spread discount on 300+ other forex pairs, with a low, fixed commission at $2.50 per $100,000 notional value, with our FX Active account.
4 0.018 seconds CFD median trade execution time on MetaTrader 4 globally, 1 April 2024-31 March 2025.
5 99.29% of MT4 market open orders were filled at quote, 23 September 2024-31 March 2025.
698.79% average core platform uptime for CMC Markets' customers trading on the MetaTrader 4 platform, January-March 2025.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...