CFD TRADING

Ready to get started?
If you already have an account, log in to your chosen platform.
Don't have one yet? Open an account now.
Log inOpen account
FX trading, also known as foreign exchange trading or forex trading is the exchange of different currencies on a decentralised global market. It’s the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Forex trading involves the simultaneous speculative buying and selling of currencies in the aim to profit.
Foreign exchange trading is also known as FX trading or forex trading provides the opportunity to speculate on price fluctuations within the FX market. FX is an industry term that is abbreviated from forex and is commonly used instead of forex. However, forex is also an abbreviation of foreign exchange.
The goal of FX trading is to forecast if one currency’s value will strengthen or weaken relative to another currency. A forex trader will encounter several trading opportunities each day, due to daily news releases. They take advantage of this by becoming extremely receptive to market news releases and then trade based upon the suspected market sentiment.
Forex is always traded in currency pairs – for example, GBP/USD (Pound sterling v US dollar). Forex trading works by speculating against the difference in valuation of two currencies.
For example, If you were to trade the GBP/USD, and thought the price of the US dollar were to drop lower than GBP, you could short sell the currency pair to profit from the difference in value.
Looking at the GBP/USD currency pair, the first currency (GBP) is called the 'base currency' and the second currency (USD) is known as the 'counter currency'. Alternatively, if you think GBP will fall against USD (or that USD will rise against GBP), you could go long.
Find out what are some of the most traded currency pairs in the forex market by reading our in-depth guide.
There are 3 different types of forex pairs:
Major pairs: Includes the most traded currencies globally and always involve the US dollar (USD) as either the base or quote currency. These pairs tend to have high liquidity
💡 Examples:
GBP/USD (British Pound / US Dollar)
EUR/USD (Euro / US Dollar)
USD/JPY (US Dollar / Japanese Yen)
Minor pairs- Do not include the US dollar but involve all the other major economies. These tend to trade at moderate liquidity
💡 Examples:
EUR/GBP (Euro / British Pound)
AUD/NZD (Australian Dollar / New Zealand Dollar)
GBP/JPY (British Pound / Japanese Yen)
Exotic Currency Pairs- consist of one major currency and one from an emerging market. These pairs have higher spreads and lower liquidity, making them more volatile.
💡 Examples:
GBP/ZAR (British Pound / South African Rand)
USD/TRY (US Dollar / Turkish Lira)
EUR/SEK (Euro / Swedish Krona)
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement a forex pair can make. Most currency pairs are quoted to four decimal places, and a pip is typically the fourth decimal place (0.0001). Traders use pips to measure price movements and calculate potential profits or losses in a trade.
If GBP/USD moves from 1.2500 to 1.2505, that’s a 5-pip movement.
For pairs that involve the Japanese yen (JPY), a pip is the second decimal place (0.01) instead of the fourth.
A lot in forex trading refers to the size of a trade. Since forex is traded in large volumes, lots standardise how much of a currency you buy or sell in one trade.
There are 3 different types of lots sizes:
Lot Size | Number of Currency Units |
Standard Lot | 100,000 |
Mini Lot | 10,000 |
Micro Lot | 1,000 |
If you trade 1 standard lot, a 5-pip move would mean $50 gained or lost.
If you trade 1 mini lot, a 5-pip move equals $5 profit or loss.
If you trade 1 micro lot, a 5-pip move equals $0.5 profit or loss.
Lot Size | Number of currency units | Pip value |
Standard Lot | 100,000 | $10 per pip |
Mini Lot | 10,000 | $1 per pip |
Micro Lot | 1,000 | $0.10 per pip |
🚨 Lot size directly affects trade risk – larger lot sizes mean bigger potential profits, but also larger potential losses. (tile)
There are many ways to trade on the forex market, all of which follow the previously mentioned principle of simultaneously buying and selling currencies. If you believe an FX ‘base currency’ will rise relative to the price of the ‘counter currency’, you may wish to ‘go long’ (buy) that currency pair. If you believe the opposite will happen and the market will fall, you may wish to ‘go short’ (sell) the currency pair.
The forex market was historically traded via a forex broker. However, with the rise of online trading companies, you can take a position on forex price movements with a spread betting or CFD trading account.
Both spread betting and CFD trading accounts provide a form of derivative FX trading where you do not own the underlying asset, but rather speculate on its price movements. Derivative trading can provide opportunities to trade forex with leverage. As this can be a risky process, forex traders often choose to carry out forex hedging strategies, in order to offset any currency risk and subsequent losses.
Read our guide on how to start trading forex.
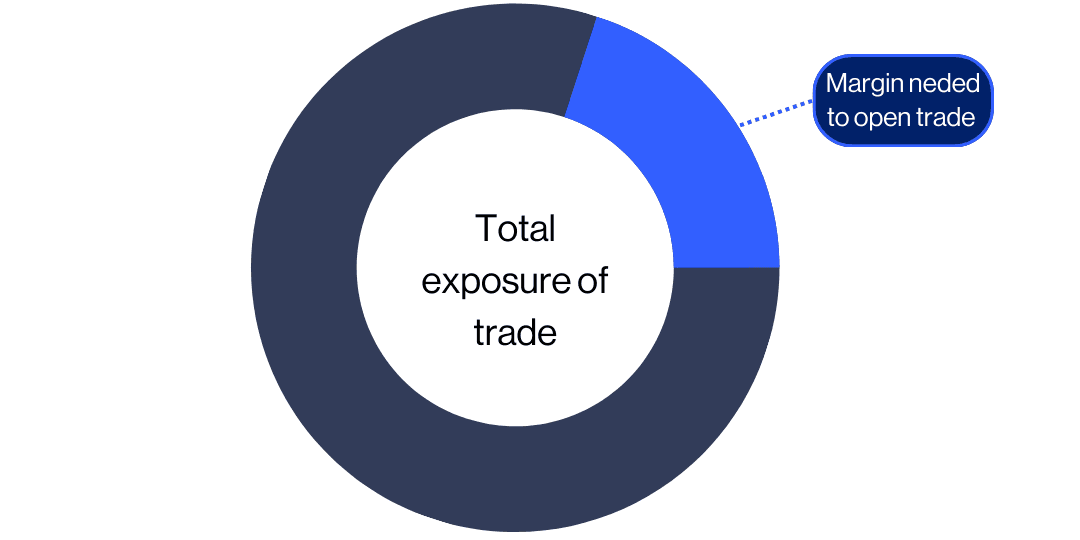
When trading, forex leverage allows traders to control a larger exposure with less of their own funds. The difference between the total trade value and the trader’s margin requirement is usually ‘borrowed’ from the forex broker. Traders can usually get more leverage on forex than other financial instruments, meaning they can control a larger sum of money with a smaller deposit.
The availability of leverage is one of the reasons that many people are interested in trading FX via a forex spread betting or CFD trading account. CMC Markets’ accounts offer competitive margin rates on forex instruments starting at just 3.3%, or 30:1 leverage. This is higher leverage than the 20% margin rate (5:1 leverage) available for shares instruments. Read about other differences between forex vs stocks here.
The spread in forex trading is the difference between the buy and sell price of an FX currency pair. When you trade forex pairs, you are presented with a ‘buy’ price that is often above the market price and a ‘sell’ price that is often below the market price. The difference between these two prices is referred to as the ‘bid-ask’, or ‘buy-sell’ spread.
Forex trading has some of the lowest spreads available of all financial instruments we offer, starting at just 0.7 points, compared to a minimum spread of 37 points for bitcoin, or 3 points for crude oil. See a full list of our current forex trading spreads and margins.
You’ve looked at the news this morning and seen some news that suggest that the pound will strengthen, so you decide to go long (buy) GBP/USD at 1.2500 with a position size of 10,000 units(1 mini lot).
Currency Pair | Buy Price |
GBP/USD | 1.2500 |
Position size | Leverage |
10,000 units (1 mini lot) | 5:1 (20% margin |
Total position value | Margin required (deposit) |
$10'000 | $2,000 (20% of $1000 |
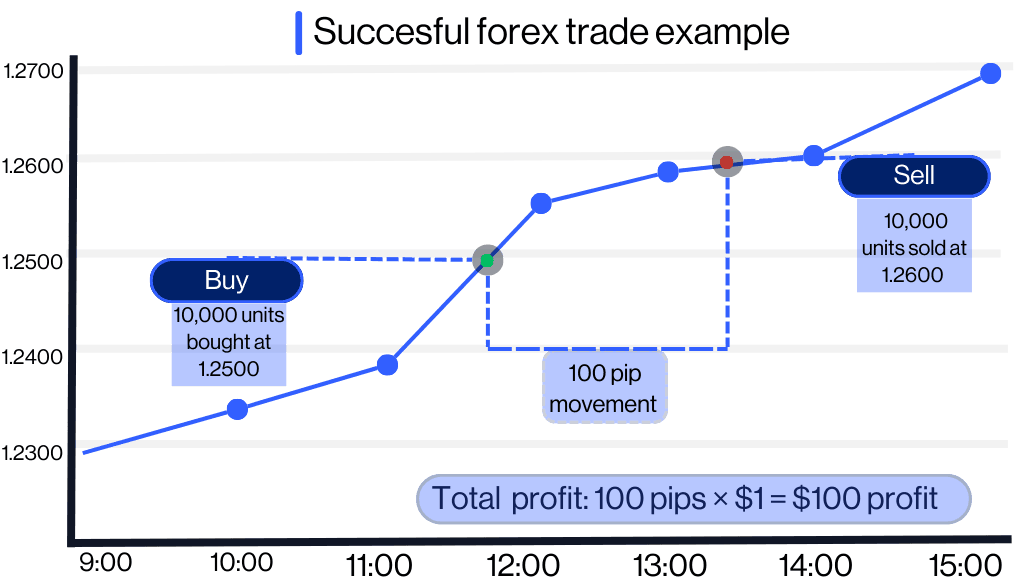
Let’s assume GBP/USD rises to 1.2600 which is a 100-pip increase (1.2600 - 1.2500 = 100 pips). From when you opened your position. You close your trade at 1.2600, locking in a profit of $100.
Pip value for 1 mini lot (10,000 units)= $1 per pip
Total Profit: 100 pips × $1 = $100 profit
Your $2,000 margin deposit remains intact, and you gain $100, leaving you with a new balance of $2,100.
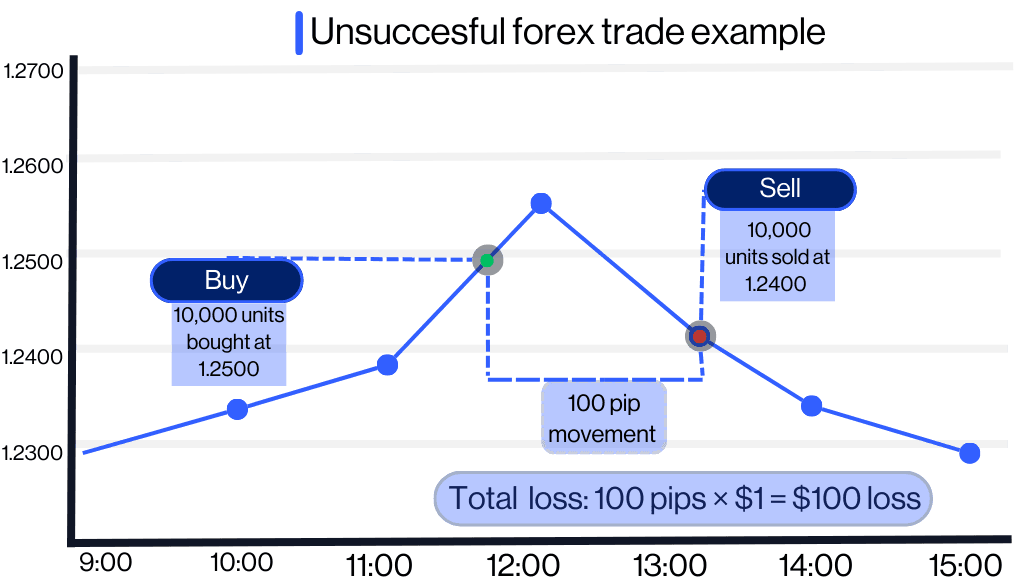
Now assume GBP/USD falls to 1.2400 (a 100-pip decrease 1.2500 - 1.2400 = 100 pips). You close your trade at 1.2400, taking a loss of $100.
Pip Value for 1 Mini Lot (10,000 units): $1 per pip
Total Loss: 100 pips × $1 = $100 loss
$100 will be taken from your $2,000 deposit you’re balance will drop to $1,900
🚨 Leverage amplifies both profits and losses while a 100-pip move resulted in $100 gain/loss, a larger position size (e.g., a standard lot) would have made this $1,000 instead.
The foreign exchange is one of the most widely traded markets in the world, with a total daily average turnover reported to exceed $5 trillion a day. The forex market is not based in a central location or exchange, and is open 24 hours a day from Sunday night through to Friday night. Read more about forex market hours here. A wide range of currencies are constantly being exchanged as individuals, companies and organisations conduct global business and attempt to take advantage of rate fluctuations.
.The foreign exchange market is used primarily by central banks, retail banks, corporations and retail traders. Understanding how each of these players interact with the FX market can help to determine market trends as part of your fundamental analysis.
Central banks are responsible for managing their nation’s currency, money supply and interest rates. When action is taken by central banks, it is usually to stabilise the nation’s currency.
Retail banks trade large volumes of currency on the interbank market. Banks exchange currencies between each other on behalf of large organisations, and also on behalf of their accounts.
Corporations that have dealt with companies overseas have to take part in the foreign exchange market to transfer funds for imports, exports or services.
Retail traders account for a much lower volume of forex transactions in comparison to banks and organisations. Using both technical analysis and fundamental analysis, retail traders aim to profit from forex market fluctuations.
To trade the forex market with little awareness of the factors that influence the FX market can result in substantial losses. Many of the macroeconomic forces at play can have huge effects on the valuation of a currency.
When looking at forex markets, it's important to remember that a stronger currency makes a country's exports more expensive for other countries, while making imports cheaper. A weaker currency makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive, so foreign exchange rates play a significant part in determining the trading relationship between two countries.
Political instability and poor economic performance can also influence the value of a currency, such as when there are presidential elections and national recessions. Politically stable countries with robust economic performance will usually be more appealing to foreign investors, so these countries draw investment away from countries characterised by more economic or political risk.
Interest rates, inflation rates and foreign currency rates are all interconnected, and as some rise others can fall. Central banks control the interest rate as a measure to control inflation. If a central bank wants to decrease inflation, it can increase interest rates in a bid to stop spending and lending. This generally increases the value of money in an economy, as there is less, or ‘more expensive’, money available in the economy.
On the other hand, when there is more money with less value in an economy, businesses and consumers increase spending and lending through loans and other types of credit. Sellers will then increase prices, causing inflation and a lower-valued currency. These fluctuations in currency value are one of the reasons forex traders may look to trade on interest rate announcements from central banks, like the US Federal Reserve or the Bank of England. This can be done through cross currency swaps, which can help to hedge currency risk on both interest rates and exchange rates.
Often paired with interest rates, inflation rates can have a major influence on a nation’s foreign exchange rates. Rising inflation rates often have a negative effect on a currency’s value. Conversely, low inflation rates usually cause an appreciation in the value of a currency. When inflation is high, the price of goods and services increases, which can cause the currency to depreciate, as there is less spending.
The terms of trade for a country represent the ratio of export prices relative to import prices. If a country’s export prices rise and its import prices fall, the terms of trade have favourably improved. This increases the nation’s revenue and is followed by an increase in demand for the country’s currency. This increase in demand can cause a rise in the currency’s value.
A nation’s debt can be a large influencer in the variations of its currency price. Countries with large debts in relation to their gross domestic product (GDP) will be less attractive to foreign investors. Without foreign investments, countries can struggle to build their foreign capital, leading to higher rates of inflation and thus, currency depreciation.
The ability to trade on forex margin (using leverage).
High levels of liquidity mean that forex spreads stay tight and trading costs stay low.
Prices react quickly to breaking news and economic announcements (this can be a disadvantage too).
Trade 24 hours a day from Sunday to Friday.
The ability to go long and short.
Wide range of markets (spread bet or trade CFDs on more than 330 forex pairs with CMC Markets).
Market trends can be more predictable.
You can lose all of your capital - leveraged forex trading means that both profits and losses are based on the full value of the position.
Risk of account close out - market volatility and rapid changes in price can cause the balance of your account to change quickly, and if you do not have sufficient funds in your account to cover these situations, there is a risk that your positions will be automatically closed by the platform.
Currency pair correlations can increase the interest rates outside of major forex pairs.
Market volatility and gapping - financial markets may fluctuate rapidly and gapping is a risk that arises as a result of market volatility, and one of the effects of this may mean that stop-loss orders are executed at unfavourable prices.
Risk of carry trade.
Central bank decisions can have an effect on interest rate levels.
Forex trading is a fast-paced, exciting option and some traders will focus solely on trading this asset class. They may even choose to specialise in just a few select currency pairs, investing a lot of time in understanding the numerous economic and political factors that move those currencies.
How do I start trading on forex?
Can I teach myself to trade on forex?
There are plenty of online resources available which can help you learn to trade forex. You can find out more about the basics from our learn forex section, which covers a wide range of topics, including margin and leverage, pips, forex market hours and forex trading strategies.
To help you get to grips with our platform and FX trading, you can open a demo account to practise with $10,000 of virtual funds.What are the 7 major currency pairs?
The seven major currency pairs make up around 75% of all forex trades worldwide. These include EUR/USD, GBP/EUR, AUD/USD and USD/CAD.
Can I trade forex without leverage?
You can’t trade forex without using leverage on our platform. If you’re concerned about the risks of leverage, there are a number of risk-management tools, such as stop-losses and take-profit orders, that could be used when placing a trade.
Which forex pairs can I trade?
What is the best forex strategy?
There isn't necessarily a 'best forex strategy', because what suits one trader might not work for another. It depends on a series of factors, as well as your own risk appetite. There are many different types of strategies, including day trading, medium-term swing trading, and very short-term forex scalping.

Explore the 16 most powerful currencies in the forex market and the economic factors that drive their dominance. Understand how GDP, trade volume, and monetary policies shape their global influence.
Understand when the forex market is open across different time zones. Learn about key trading sessions and how market hours affect liquidity and volatility.

Learn the essential steps to start trading forex, from choosing a currency pair to opening your first trade.
Disclaimer: CMC Markets is an execution-only service provider. The material (whether or not it states any opinions) is for general information purposes only, and does not take into account your personal circumstances or objectives. Nothing in this material is (or should be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by CMC Markets or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person. The material has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research. Although we are not specifically prevented from dealing before providing this material, we do not seek to take advantage of the material prior to its dissemination.