Benefits of options trading
Options trading is known for its relatively complex nature and the diverse strategies it presents. Whether you're looking to hedge against an existing investment or trade on market volatility, options can offer traders possible opportunities.
Advantages of options
Historically, options have been used in various cultures to secure the price of goods or commodities for future delivery.
Key potential advantages of options trading include:
Variety of strategies: Whatever your trading style, options provide a range of strategies to cater to different risk profiles and market outlooks.
Risk mitigation: Know your potential loss upfront – the maximum loss for buying a call or put option is limited to the premium paid.
Use of leverage: Trading options contracts for difference (CFDs) allow traders to control a large amount of stock for a fraction of its price without owning it, amplifying potential gains, as well as losses.
Speculate: Options enable traders to profit from price movements in the underlying asset, whether they anticipate it going up or down.
Hedging: By trading on options, investors can protect their underlying stock portfolio investment from adverse price movements through hedging.
Variety of strategies
Options trading offers a range of strategies. We look at four popular options trading strategies, shedding light on how they work and their potential benefits.
Cash-secured puts
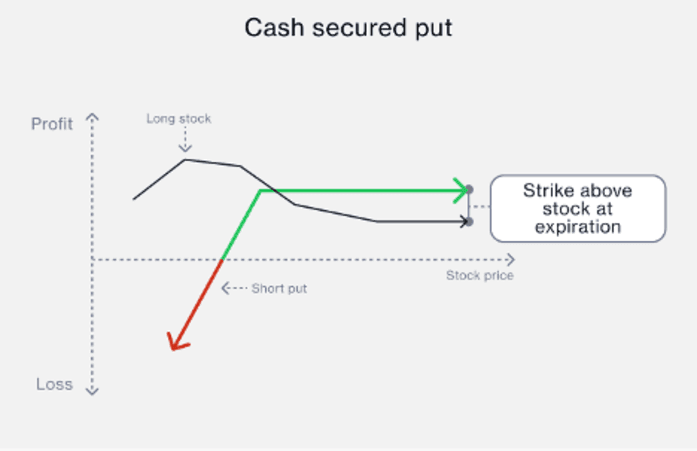
Cash-secured puts involves selling a put option while simultaneously setting aside the funds to purchase the stock if it drops to the option's strike price.
If the stock stays above the strike price, the put option will expire worthless, and you keep the premium paid to open the position. If the stock falls below the strike price, you will be obligated to buy the stock at the strike price, but get to keep the premium.
This is a way to speculate on price movements or to potentially buy a stock at a lower price, while also keeping the premium paid.
Covered calls
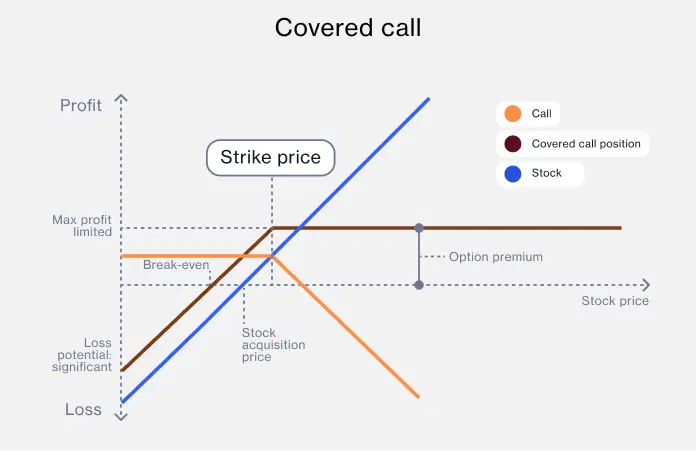
Covered calls are a strategy where you hold a long position in a stock and sell (write) call options on that stock. You earn a premium from selling the call, but the potential upside is capped if the stock rises beyond the call's strike price.
This strategy provides an income stream on top of any dividends or gains from the stock, but limits the upside potential.
Short strangle
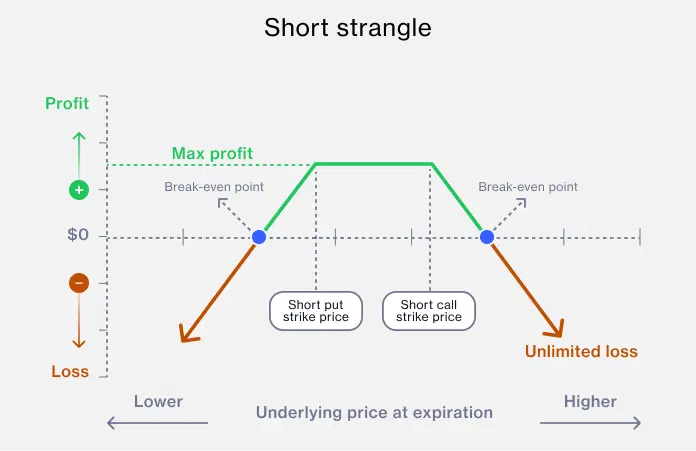
Short strangle involves selling an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put on the same stock with the same expiration date.
When you sell an option, you receive a premium from the buyer. In a short strangle, you collect premiums from both the call and the put options you sell. The total income you receive from selling these options is known the "premiums collected."
The maximum profit in this strategy is limited to the premiums collected, because once you've sold the options, the most you can gain is the income from the premiums. There's no other source of profit in this position.
This maximum profit is realized if the stock price stays between the strike prices of the call and put options until expiration. In this scenario, both options expire worthless, and you get to keep the entire premium as profit. Losses can occur if the stock moves significantly in either direction.
You can profit in a neutral market if the stock stays between the two strike prices. It's a strategy aimed at generating income in range-bound markets.
Long straddle
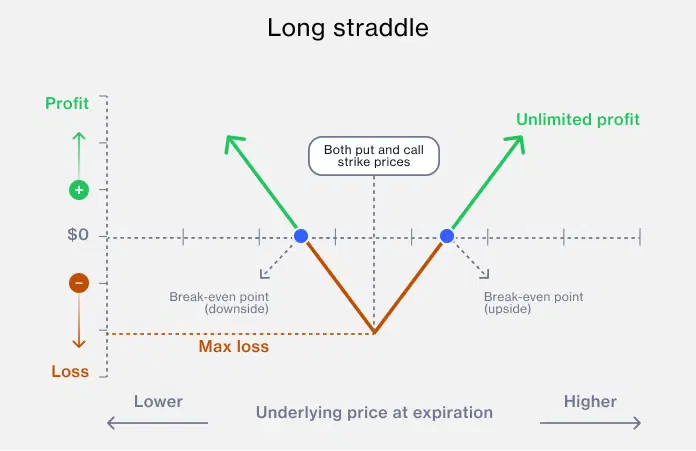
Long straddle is where you buy both a call and a put option on the same stock with the same strike price and expiration date. You profit if the stock moves significantly in either direction. The maximum loss is limited to the combined premiums paid for the options.
This strategy allows traders to profit from big price swings, whether upwards or downwards. It's a bet on volatility rather than a specific price direction.
These are just a handful of strategies available in options trading. Each have their own nuances, based on specific market conditions and trader objectives. As with all trading methods, it's crucial to understand each strategy fully and consider your risk tolerance.
Managing your risk
Options are used by some traders as a means of mitigating risk.
Defined risk: When you buy an option, the most you can lose is the premium you paid. No matter how the market moves, your potential loss is capped. However, the option will expire worthless if the market doesn’t move enough to be in-the-money, so if you have multiple option positions which aren’t in-the-money, your overall losses will accumulate.
Protection from price drops: Options are often regarded as a more dependable hedge compared to stocks. When traders buy stocks, they may use a regular stop-loss order to limit potential losses. This order is set to sell the stock if its price drops to a certain level. However, it will only take effect when the stock hits or goes below the pre-set price during market hours.
In contrast, options offer a safety net even when the market is closed, whereas a stop-loss order might not always execute at the expected price due to unforeseen market events.
Flexibility: Options allow you to make money whether the market is going up, down, or staying flat. This presents more potential opportunities to profit and diversify.
Hedging: By trading on options strategically, you can protect your wider investments from adverse market movements.
Leverage: Trading options on leverage allows traders to gain greater market exposure through a comparatively small initial payment, known as the premium. This means traders can enter a position without committing to the full cost upfront.
Hedging
A long-put option can be used as a type of insurance against a drop in the price of an asset you already hold a position in. Using options to hedge can reduce short-term risk and limit any losses – with the benefit being that it could generate additional profit.
You may be able to buy a put option directly on the asset you hold, or on an index which is closely correlated to your portfolio, known as a proxy hedge. The goal is to offset any losses that may occur in your portfolio if there are adverse movements in the underlying market.
Example of options hedging
Your investment portfolio consists of one share of the S&P 500 which is currently trading at $4,000. After a news announcement you identify the risk of a potential market downturn that could negatively impact the value of your portfolio.
You decide to mitigate the risk by purchasing a European-style cash-settled put option on the S&P 500 index. The strike price of the put option is set at $3,900, with an expiry date three months from now.
The contract stipulates that if the S&P 500 index falls below $3,900 by the expiry date, you can exercise the right to sell the index at the strike price of $3,900 to the contract writer. If the S&P 500 remains above $4,000, you let the option expire and only lose the premium paid.
If the S&P 500 falls below the strike price of $3,900, the contract will be exercised at expiration, and you will receive a cash payment for the difference between the underlying S&P 500 level and the strike price. This gain will partially offset the decline in your investment portfolio.
By paying a premium upfront, you’ve protected your portfolio from the adverse effects of declining market conditions, ensuring a degree of stability and risk mitigation.
Options are different to a stop-loss order, which automatically kicks in at a certain price level. Options offer the choice of exiting the trade, with the bonus of being able to hold fire for the duration of the option to see if the market recovers.
Risks and challenges of options trading
Trading options is based on backing an asset to move in a particular direction, within a specific timescale.
Particularly with long options, if the underlying asset doesn’t perform as hoped in the stipulated timeframe, and the trader lets the contract expire, the premium cost will be lost. This loss may not be significant in itself, but if the same thing keeps happening, those losses can accumulate.
There is also the risk of external factors affecting option value, most importantly volatility, which will affect both long and short options. Higher volatility increases the value of long call and put options, as it raises the likelihood of substantial price movements, making these options more valuable due to greater potential for profitability.
Conversely, for short call and put options, high volatility is a greater risk, as it increases the chances of significant price swings in the underlying asset, making it more likely the options will be exercised against the seller, potentially leading to losses.
On the other hand, lower volatility decreases the value of long options, as the expected price movement of the underlying asset is less dramatic. However, it benefits short options by reducing the risk of the options being exercised, ultimately favouring the seller's strategy of options expiring worthless.
You can choose to do this at any time up to the expiry (for American options) or on the expiry date (for European options) of the contract. Positions can be closed at any time, in line with your trading strategy.
Cash-settled options will automatically be exercised at expiration if it’s in the money, generating a positive outcome for the buyer.
If an option expires out of the money, it won’t be exercised. The buyer’s maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the contract.
Any questions?
Email us atWe're available whenever the markets are open, from Sunday night through to Friday night.




