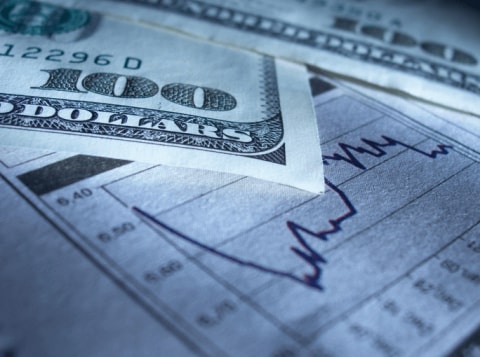
Forex signals are popular and innovative financial tools that can help you trade forex pairs. Forex signals, which are generated either by an automated program or by a trader, identify the best time to enter or exit a trade. A forex trading signal is essentially an alert for traders to either enter or exit a position (go long or go short). Forex signals are often based on specific times and prices and can be identified through technical or fundamental analysis. It is up to the trader to then decide whether or not to act on the signal.
It should be mentioned that, in a fast and liquid market like the forex market, a forex signal is helpful only if used at the right time. If received too late, the signal might become unreliable. Read on to discover the different types of forex signal, along with how to use them when trading currency pairs.